STD Treatment in Malaysia
Specialised GPs for STD Treatment in Malaysia
In Malaysia, STD treatment typically involve a collaborative approach between various healthcare professionals, including general practitioners (GPs) with specialised knowledge in dermatology.
Enhanced Convenience
Our patients can conveniently receive comprehensive dermatological care directly from their GP, eliminating the need for separate appointments with dermatologists.
Prompt Treatment
With our extensive knowledge in dermatology, patients can expect prompt and efficient treatment without the typical delays associated with referrals and scheduling with specialists.
Cost Savings
By efficiently managing the majority of dermatological cases in-house, we significantly reduce the frequency of referrals to dermatologists, ultimately resulting in potential cost savings for our patients.

About Dr. K & Associates Clinic
Common STDs
At Dr. K & Associates Clinic, patients with HIV will be referred to a tertiary hospital that can provide the appropriate and specialised treatment they require.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
Syphilis
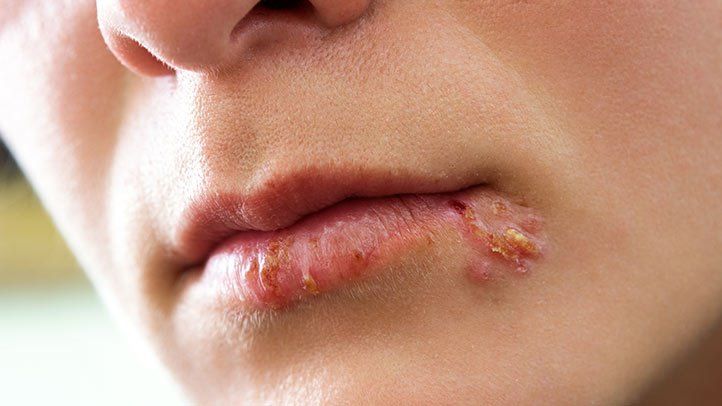
Herpes
Gonorrhoea
Chlamydia
Trichomonas
Understanding the Varied Forms of STDs
Genital Symptoms
- Abnormal genital discharge
- Genital sores or ulcers
- Itching or irritation
- Pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse
- Testicular or pelvic pain
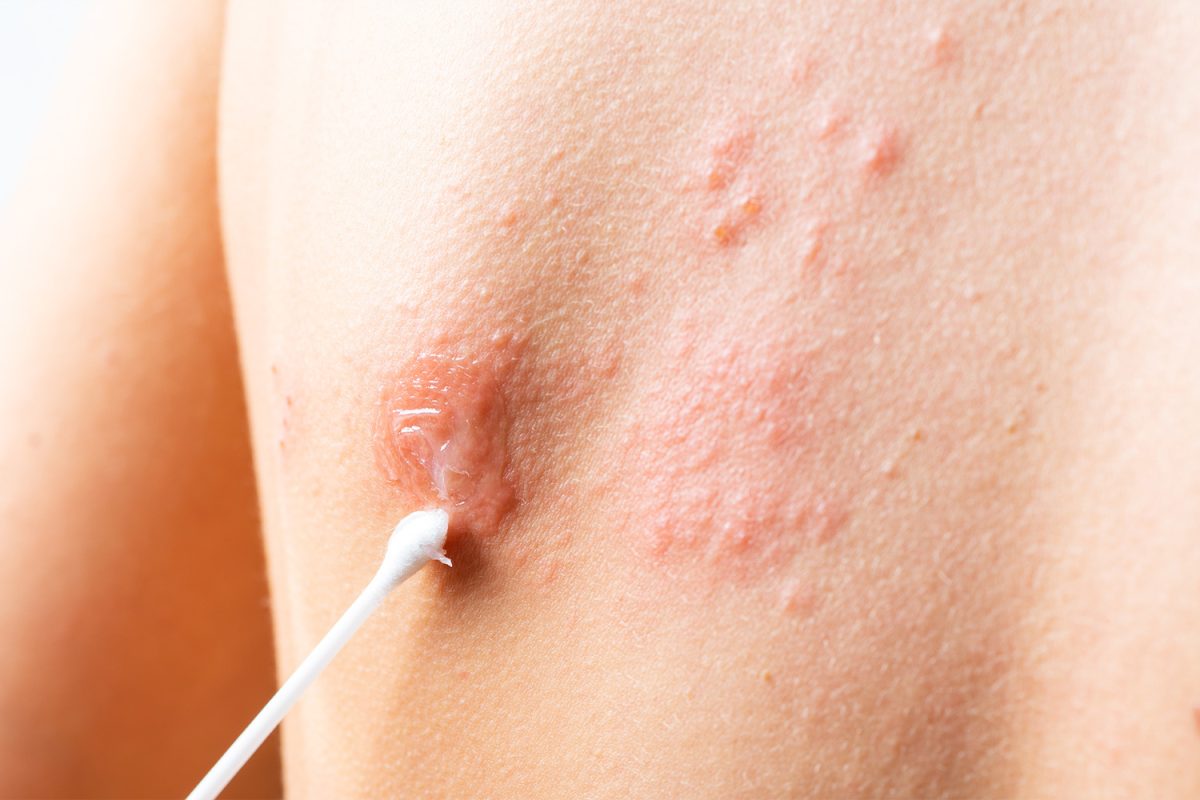
Skin Symptoms
- Rashes
- Lesions or bumps
- Sore throat or mouth ulcers
Urinary Symptoms
- Pain or burning during urination
- Frequent urination
- Blood in urine
STD Screening Methods
Blood Tests

Urine Tests
Swab Tests
Blood Tests

Urine Tests

Swab Tests

Blood Tests

Urine Tests

Swab Tests

STD Treatments
Effective treatment of STDs is essential for managing infections, alleviating symptoms, and preventing further transmission. Various treatment options are available depending on the specific STD and individual circumstances, including:
Topical Medications
Certain STIs, such as Herpes and genital warts, can be treated with topical creams or ointments applied directly to the affected area. These medications help alleviate symptoms, reduce the duration of outbreaks, and prevent the spread of the infection.
Laser Surgery Therapy
Injections or Oral Medications
Vaccinations for STI Prevention

HPV (Gardasil 9)

Hepatitis B
Topical Medications
Certain STIs, such as Herpes and genital warts, can be treated with topical creams or ointments applied directly to the affected area. These medications help alleviate symptoms, reduce the duration of outbreaks, and prevent the spread of the infection.
Laser Surgery Therapy
Injections or Oral Medications
Vaccinations for STI Prevention

HPV (Gardasil 9)

Hepatitis B

Meet Our Doctor
Dr Kimberly Yap Hae Mun
Founder and Medical Director

- Doctor of Medicine, M.D (Russia)
- Letter of Credentialing & Privileging (LCP) Board Certified
- Diploma of Aesthetic Medicine (USA)
- Diploma of Dermatology (Australia)
- Lifetime Member of Malaysia Medical Association (MMA)
- Member of the Academy of Family Physicians of Malaysia (AFPM)
- Member of PDEBM (Pertubuhan Doktor Estetik Berdaftar Malaysia)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The permanence of STD treatments can vary depending on the specific STD and the individual’s circumstances.
Some STDs can be effectively cured or treated with appropriate medical interventions, resulting in a permanent resolution of the infection. For example, bacterial infections like Chlamydia and Gonorrhoea can typically be treated and cured with antibiotics.
However, there are certain viral STDs, such as HIV, Herpes, and Hepatitis B, that currently do not have a cure. Treatment for these viral infections focuses on managing symptoms, reducing the risk of transmission, and controlling the disease to prevent complications.
Our doctors are general practitioners who have received specialised training and possess a strong interest in practical dermatology. This allows them to effectively address a broad range of dermatological concerns, including acne, rashes, eczema, psoriasis, and infections.
If you suspect that you may have contracted a sexually transmitted disease, it is crucial to seek medical assistance from your general practitioner (GP) or a local STD clinic. Most STIs can be successfully treated, but it’s important to have any symptoms evaluated as soon as possible to ensure timely intervention and appropriate care.
If left untreated, STIs can cause severe health complications. These complications include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), an increased risk of acquiring HIV, certain types of cancers, and even infertility.
It is crucial to seek timely medical attention and appropriate treatment for STIs to prevent these potentially severe consequences.
STIs can affect anyone who engages in sexual activity, regardless of age, gender, or sexual orientation. Factors that contribute to the transmission of STIs include:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse (vaginal, anal, or oral)
- Having multiple sexual partners
- Engaging in high-risk sexual behaviours